Volunteers are the heart of Rally's mission!

Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor (AT/RT) is a rare and fast-growing tumor that typically originates in the brain and spinal cord. These...

Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a brain tumor found in a part of the brain stem—above the back of the neck and connected to the...

Medulloblastoma is a type of brain cancer that’s most commonly found in children. “Medulloblastoma starts in the cerebellum, which is...
“Glioma” is a general term for a group of tumors that begin in glial cells—the supporting cells of the brain. Gliomas are classified based...
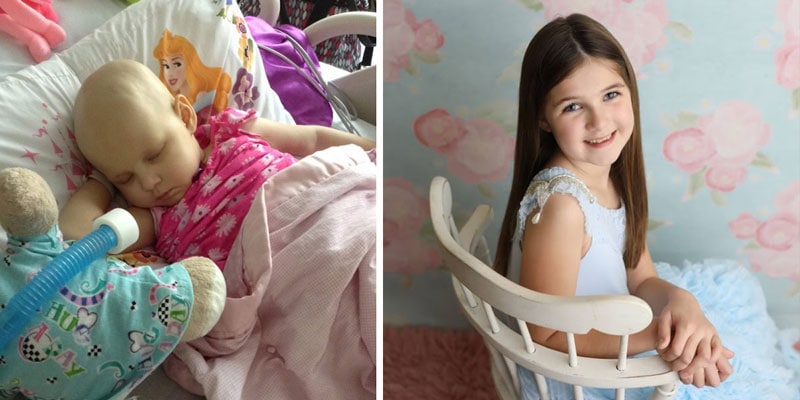

Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, also called acute lymphocytic leukemia, or ALL for short, is a type of blood cancer that causes bone marrow...

Wilms tumor is a type of kidney cancer that primarily develops in children around the ages of three and four. It’s the most common type of...
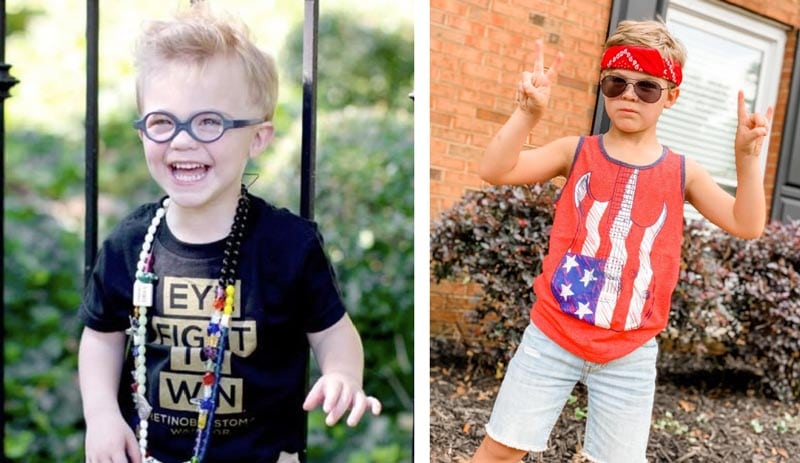

In simple terms, retinoblastoma is an eye cancer that develops in the immature cells of the retina. Though it is rare—with approximately...
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a blood cancer of the myeloid cells that normally form white blood cells, red blood cells or platelets....

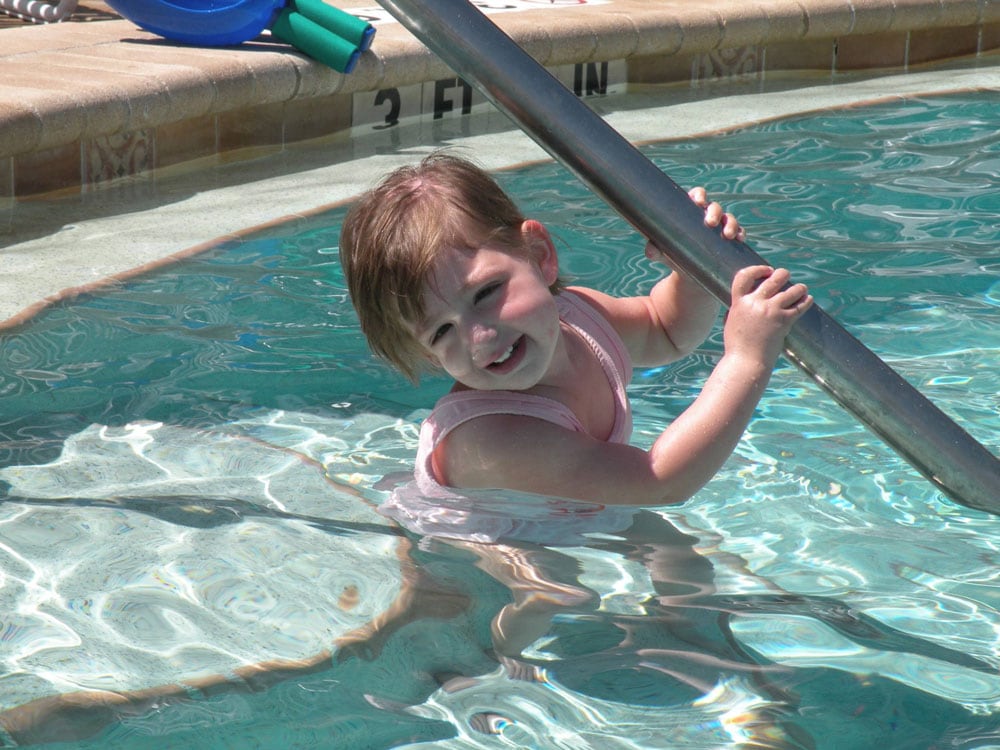
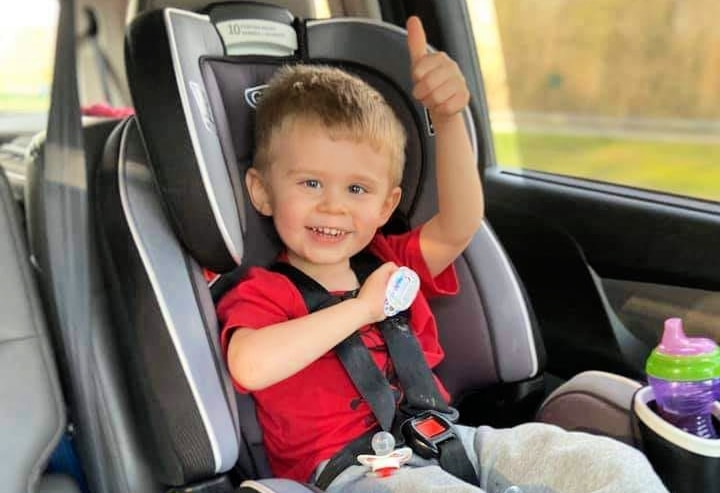
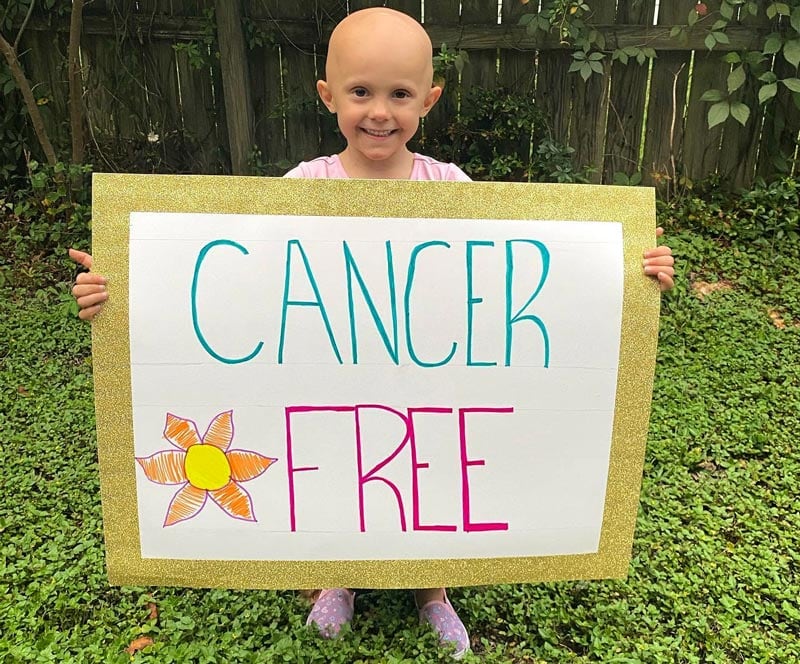
Childhood cancer is a big problem. In the U.S. alone, 46 children are diagnosed with cancer every school day. But it doesn’t just affect...
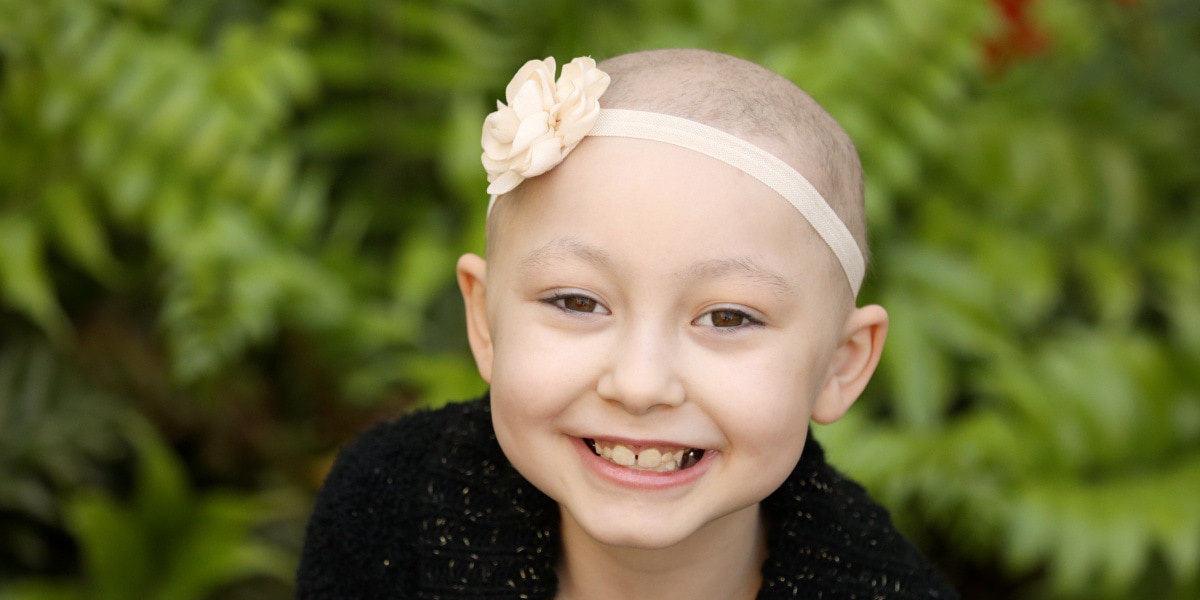

It’s no secret that adults get cancer. But children get cancer, too -- and it’s more common than you might think. Worldwide, 300,000 kids...
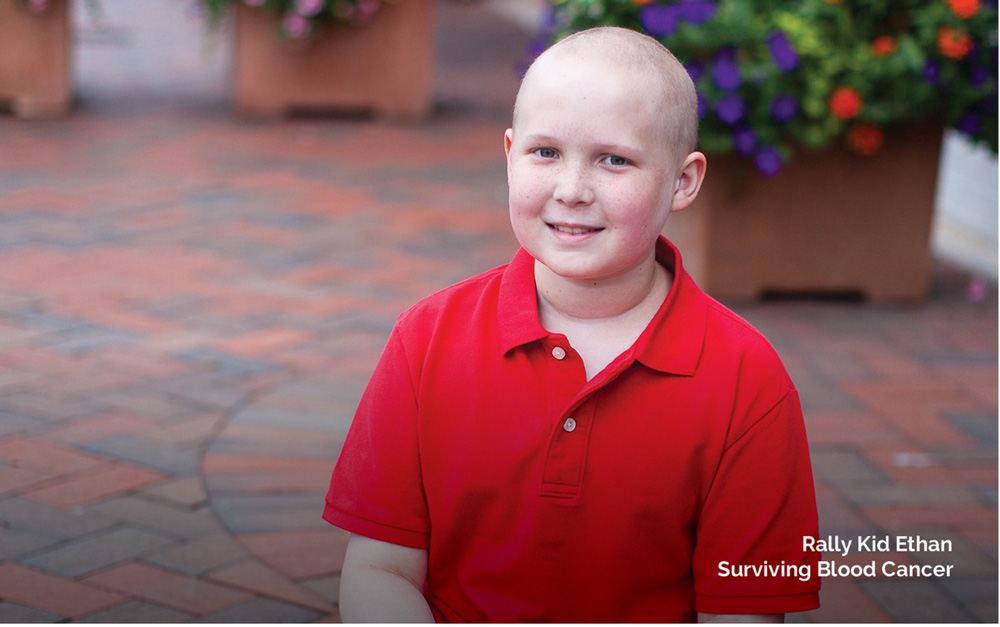

Lymphoma is a cancer of the body’s lymphatic (lymph) system which is essential to the immune system. The lymphatic system is made up of a type of white blood cells also known as lymphocytes which flow throughout the whole body. These lymphocytes fight infections throughout the body, so when cancerous cells begin to grow they can quickly spread through the entire lymph system. This then makes it difficult for the immune system to work properly. Early symptoms of lymphomas usually begin with a...
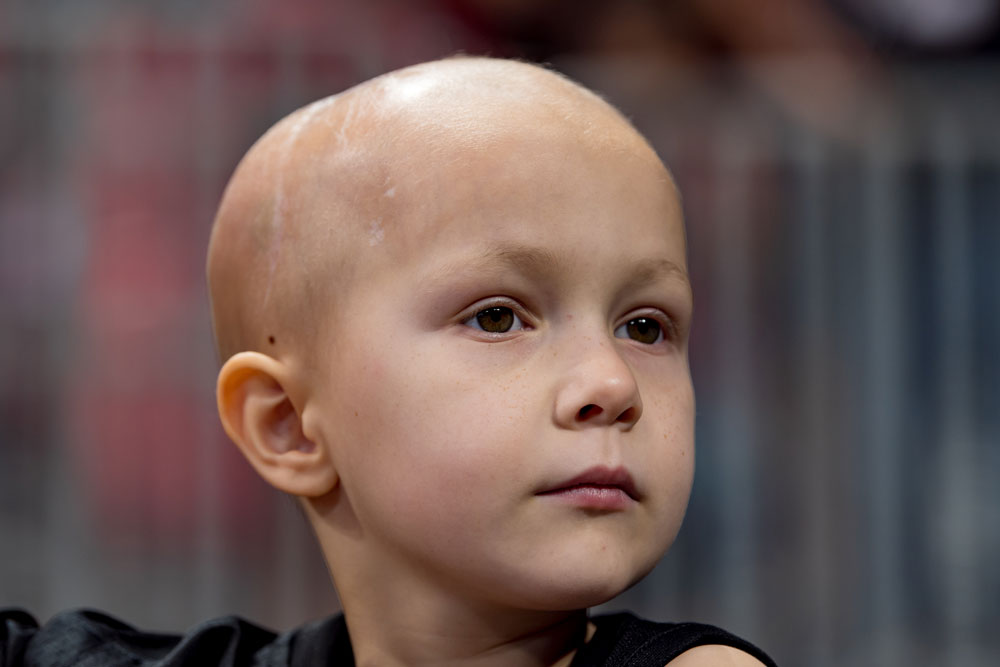

Ependymoma is a tumor that appears most often in the brain and sometimes in the spinal cord. It is a type of glioma, meaning it starts in the support cells of the brain. This cancer occurs more frequently in children—accounting for 5-10% of all pediatric brain tumors—but it can also affect adults. Common pediatric subtypes include classic ependymoma, a tumor that most commonly appears in the brain, and anaplastic ependymoma, which tends to spread and has a high chance of recurrence. Each type...

Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a type of blood cancer that causes an overproduction of white blood cells. These cells grow abnormally and can build up in the blood and bone marrow, leaving less room for healthy white and red blood cells as well as platelets. CML is commonly associated with a genetic mutation called the Philadelphia chromosome. While CML is very rare in children, with about 150 pediatric cases in the U.S. each year, it’s often more aggressive in kids than it is in adults....
Neuroblastoma is a cancerous tumor that develops in the nervous system of babies and young children. It can also occur, rarely, in adolescents. A neuroblastoma tumor often affects immature nerve tissue called neuroblasts. The most common area for neuroblastoma to appear is in the adrenal glands, which sit above the kidneys. Adrenal glands produce hormones that control body functions such as digestion, blood pressure, breathing and heart rate. Neuroblastoma can also begin in other areas of the...

Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor (AT/RT) is a rare and fast-growing tumor that typically originates in the brain and spinal cord. These tumors most often occur in the part of the brain called the cerebellum, which controls movement and balance, or in the brain stem, which controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate. AT/RT mainly occurs in children under the age of three, but it can occur in older children and very rarely in adults. AT/RT is found in fewer than 3% of children with...

Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a brain tumor found in a part of the brain stem—above the back of the neck and connected to the spine—called the pons. The pons is a vital part of the brain, controlling critical bodily functions like breathing, swallowing, blood pressure, heart rate, eyesight and balance. DIPG occurs almost exclusively in children; most often between the ages of four and 11. DIPG accounts for roughly 10-15% of all brain tumors in children. These tumors—called gliomas...