It’s no secret that adults get cancer. But children get cancer, too -- and it’s more common than you might think. Worldwide, 300,000 kids...


It’s no secret that adults get cancer. But children get cancer, too -- and it’s more common than you might think. Worldwide, 300,000 kids...

Ewing Sarcoma Defined Ewing sarcoma is a cancerous bone tumor that affects children, adolescent and young adults—usually developing during...

Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a type of soft tissue cancer that most commonly affects children and adolescents. It’s often found in skeletal...
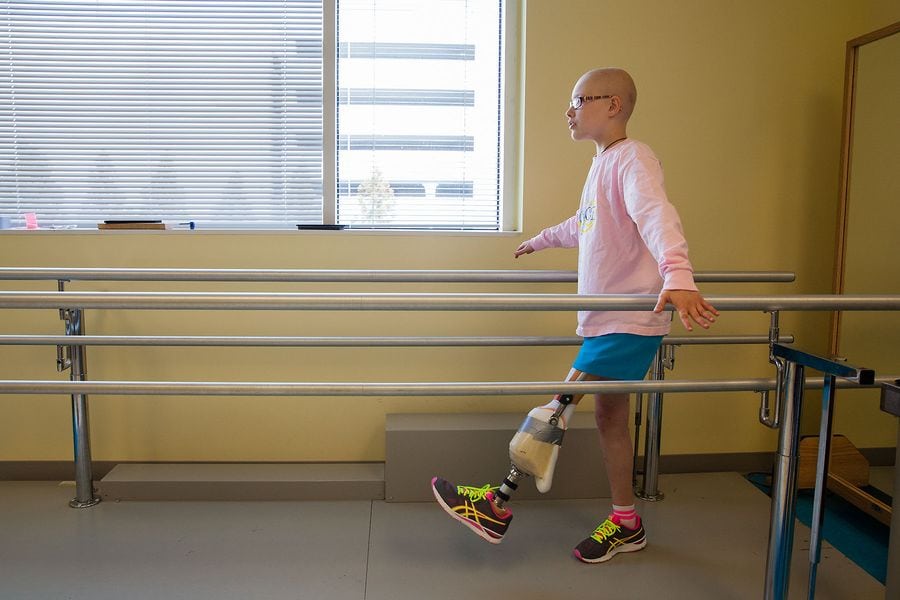
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer in children and adolescents. The tumor often originates in the long bones of the body,...
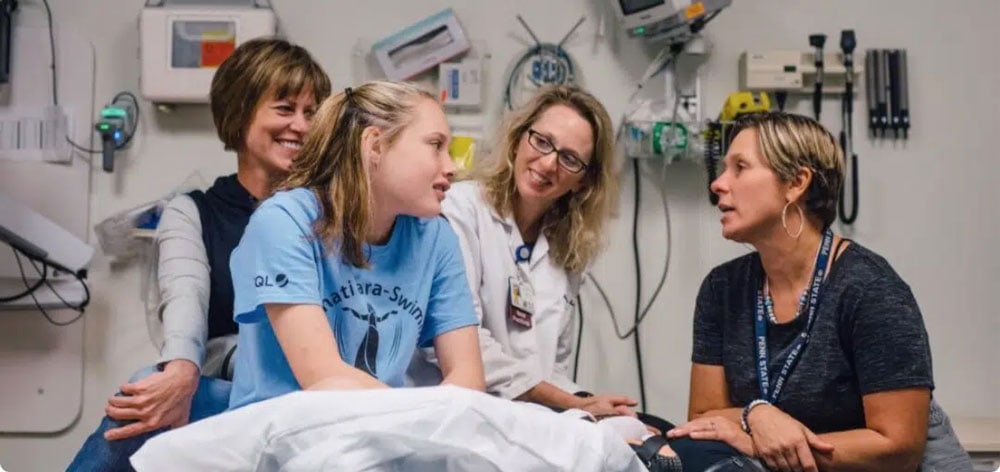

OSI Connect is a free, easy-to-use, invaluable resource for those diagnosed with osteosarcoma Osteosarcoma is a difficult and frightening...
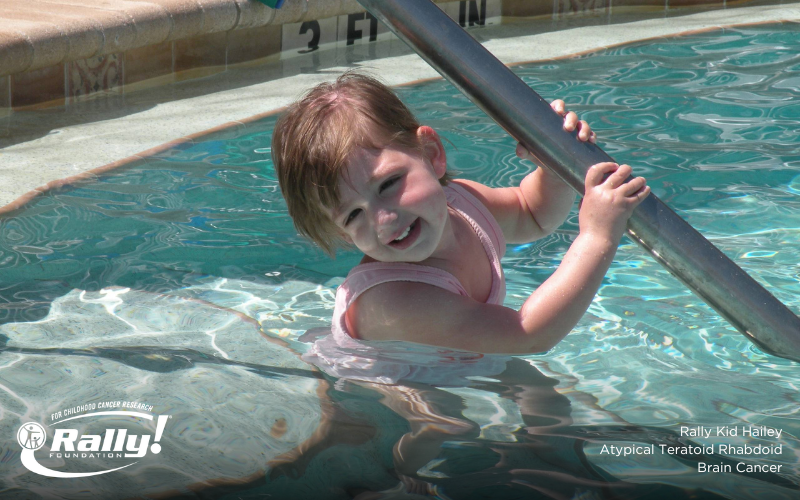

Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor (AT/RT) is a rare and fast-growing tumor that typically originates in the brain and spinal cord. These tumors most often occur in the part of the brain called the cerebellum, which controls movement and balance, or in the brain stem, which controls vital functions like breathing and heart rate. AT/RT mainly occurs in children under the age of three, but it can occur in older children and very rarely in adults. AT/RT is found in fewer than 3% of children with...
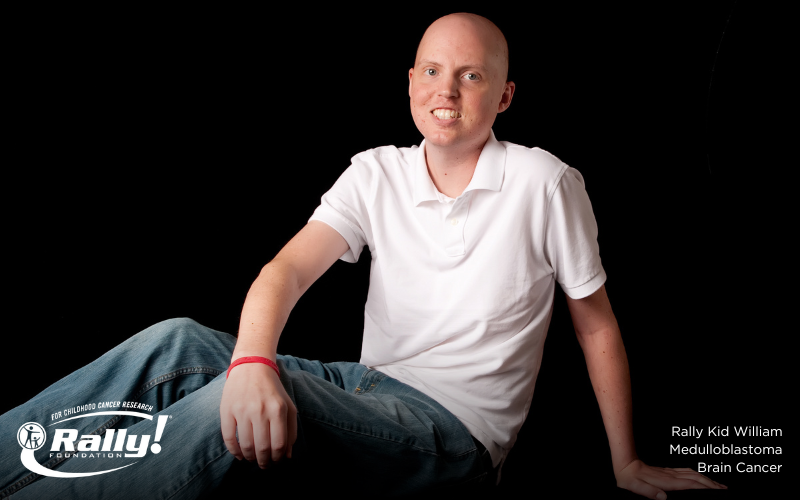

Medulloblastoma is a type of brain cancer that’s most commonly found in children. “Medulloblastoma starts in the cerebellum, which is located in the back of the brain,” explained Rally-funded Researcher Dr. Jezabel Rodriguez-Blanco, Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics at the Medical University of South Carolina. “It is a fast-growing tumor that often compresses the ventricle that brings the protective cerebrospinal fluid to the brain. The cerebellum is the part of the brain that...
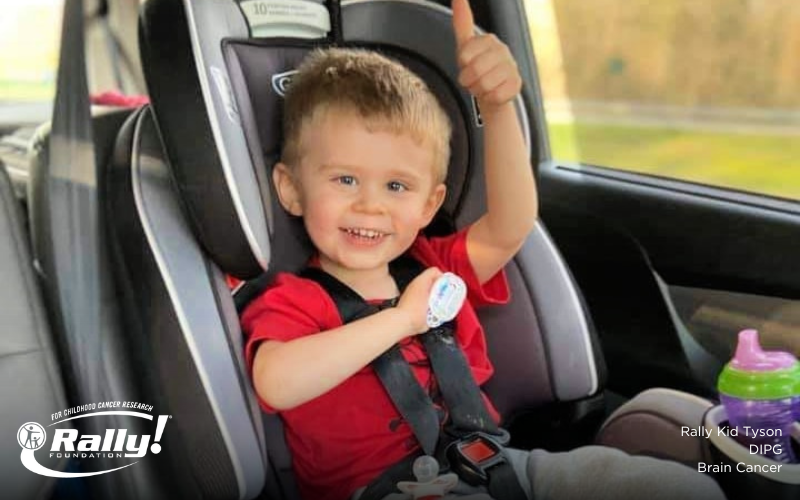

Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) is a brain tumor found in a part of the brain stem—above the back of the neck and connected to the spine—called the pons. The pons is a vital part of the brain, controlling critical bodily functions like breathing, swallowing, blood pressure, heart rate, eyesight and balance. DIPG occurs almost exclusively in children; most often between the ages of four and 11. DIPG accounts for roughly 10-15% of all brain tumors in children. These tumors—called gliomas...
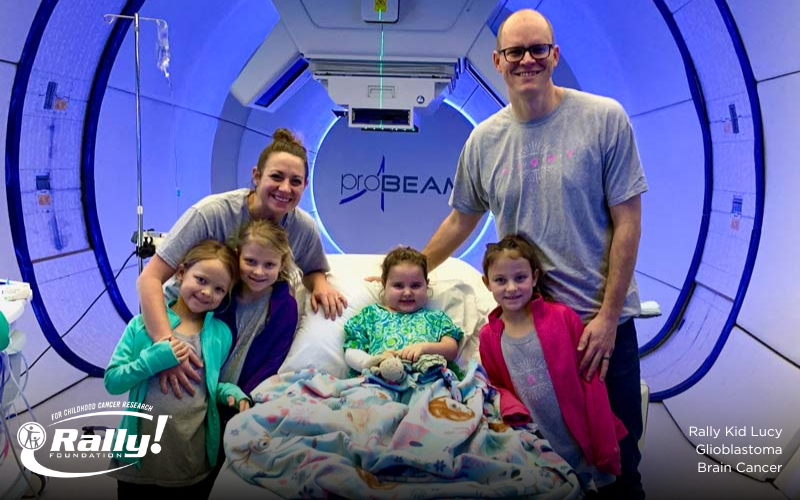

“Glioma” is a general term for a group of tumors that begin in glial cells—the supporting cells of the brain. Gliomas are classified based on their location and by the type of glial cell—astrocytes, oligodendrocytes or ependymocytes—from which they arise. Thus, many different types of brain tumors are classified as gliomas, like astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, ependymomas, brain stem gliomas and glioblastomas. About half of all pediatric brain and spinal cord tumors are gliomas. Gliomas are...
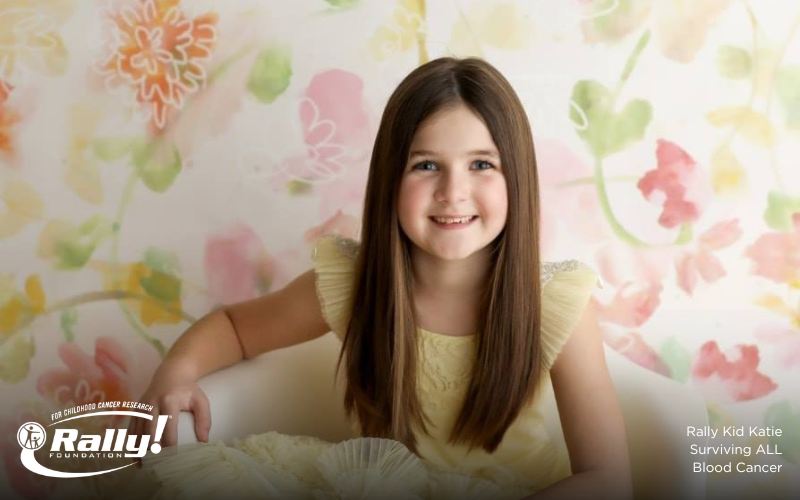

Acute lymphoblastic leukemia, also called acute lymphocytic leukemia, or ALL for short, is a type of blood cancer that causes bone marrow to overproduce a type of white blood cells called lymphoblasts. ALL is the most common type of cancer that affects kids, accounting for roughly 30% of all cases of childhood cancer. Lymphoblasts are immature white blood cells that are responsible for identifying and destroying foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. When someone has ALL, the bone marrow...
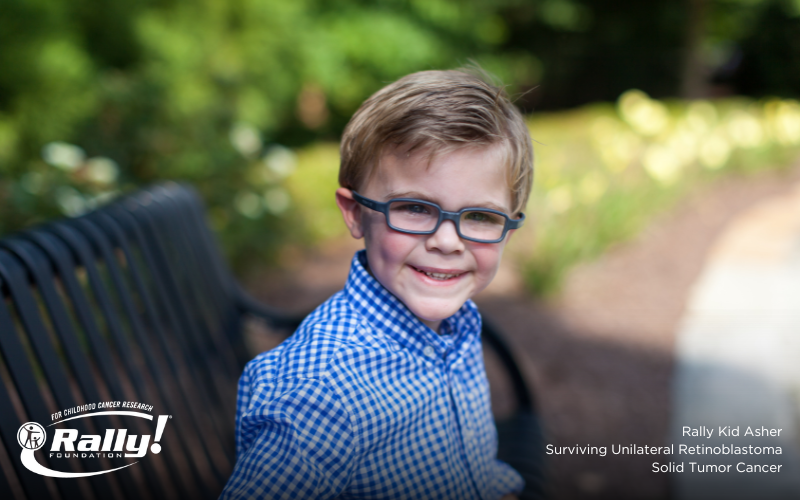

In simple terms, retinoblastoma is an eye cancer that develops in the immature cells of the retina. Though it is rare—with approximately 300 children diagnosed in the U.S. each year—it is the most common eye cancer in children. This malignant intraocular cancer rarely occurs in adults. Retinoblastoma can occur in one or both eyes and is caused by genetic mutations in the nerve cells of the retina. The retina is comprised of nerve tissue and is the part of the eye that’s responsible for sensing...