No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
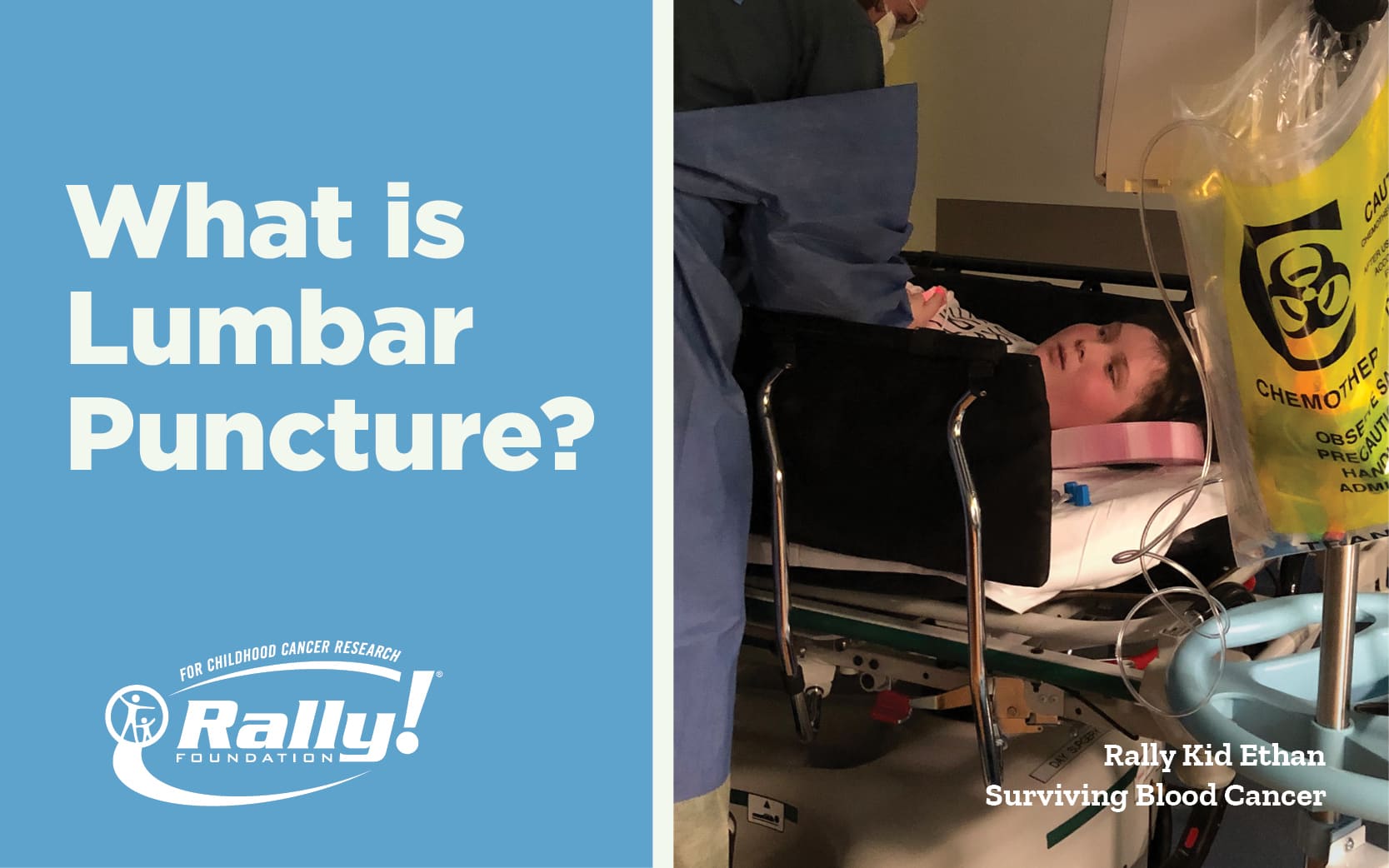
It’s scary enough to have your child diagnosed with cancer. But on top of that you hear all these new words and terms, which can be overwhelming, such as lumbar puncture or spinal tap. A lumbar procedure is the same thing as a spinal tap. It is a commonly performed procedure to diagnose and manage a variety of diseases including cancer. It is an invasive procedure used to collect the cerebral fluid that surrounds the brain and the spinal cord. A lumbar puncture/spinal tap may also be done to...

You just found out that your child has cancer. And that chemotherapy is part of the treatment plan. Most everyone has heard of chemotherapy. But what is it really? Chemotherapy is any drug used to stop the growth of cancer cells. Chemotherapy is designed to either kill cells or stop them from dividing. Is there just one chemotherapy? There are many different types of chemotherapy because different chemotherapies treat different types of cancer. Sometimes your child may receive several...

Radiation therapy is targeted energy used to destroy cancer cells, shrink tumors and/or alleviate certain cancer-related symptoms. Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays and other forms of radiation therapy to damage the DNA in cancer cells, killing them or depriving them of their ability to grow or divide. Radiation can be used in several ways: Primary treatment to destroy cancer cells In combination with other treatments to stop the growth of cancer cells Before another treatment to...
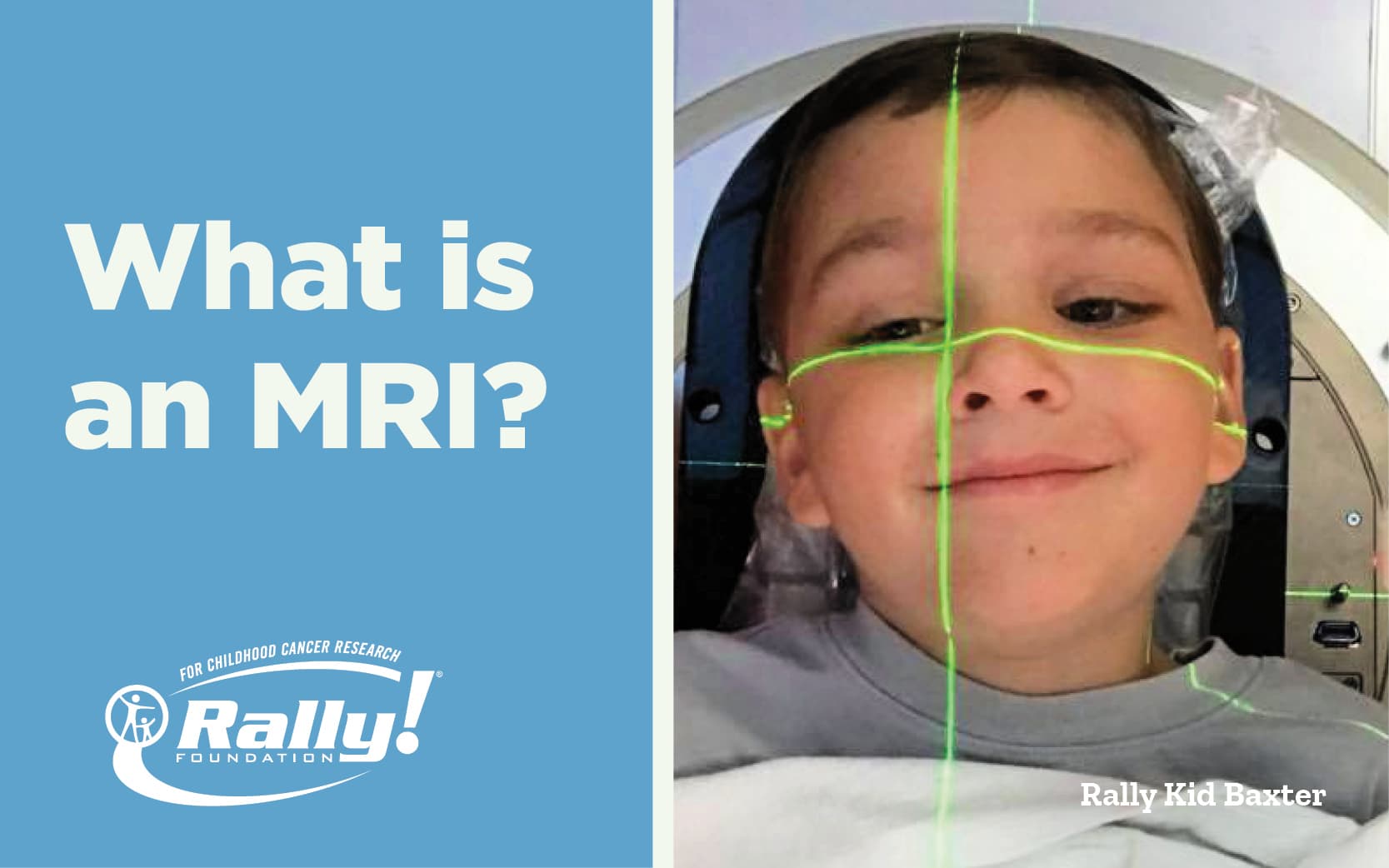
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Having an MRI does not hurt, and it is safe – no radioactivity is present. It may take up to one hour, or, if your child needs an anesthetic, most of the day. An MRI scan provides diagnostic information not available when using plain X-rays, ultrasounds, or CT scans. Using a large magnet, radio waves and a computer, an MRI scanner creates very clear and detailed images of organs and tissues in the body. During the MRI, your child will need to lie very...

A CT (or CAT) scan is a diagnostic medical imaging procedure that creates three-dimensional images of internal organs, soft tissues, blood vessels and bones. CT stands for Computed Tomography. It provides a more detailed image than a traditional X-ray. Most CT scans take a few seconds, while some may take more than 10 minutes. The CT scanner looks like a giant donut with a sliding bed inside, and your child needs to lie very still during the procedure. It’s important to wear comfortable,...

A blood transfusion is a routine medical procedure to transfer blood (or a specific component of blood) from one person to another. Blood has several components, including: Red cells that carry oxygen and help remove waste products; White cellsthat help your body fight infections; Plasmais the liquid part of blood; and Plateletshelp blood clot properly. Blood transfusions can save lives. They are a treatment for certain diseases, including blood cancers. Receiving a platelet transfusion is...