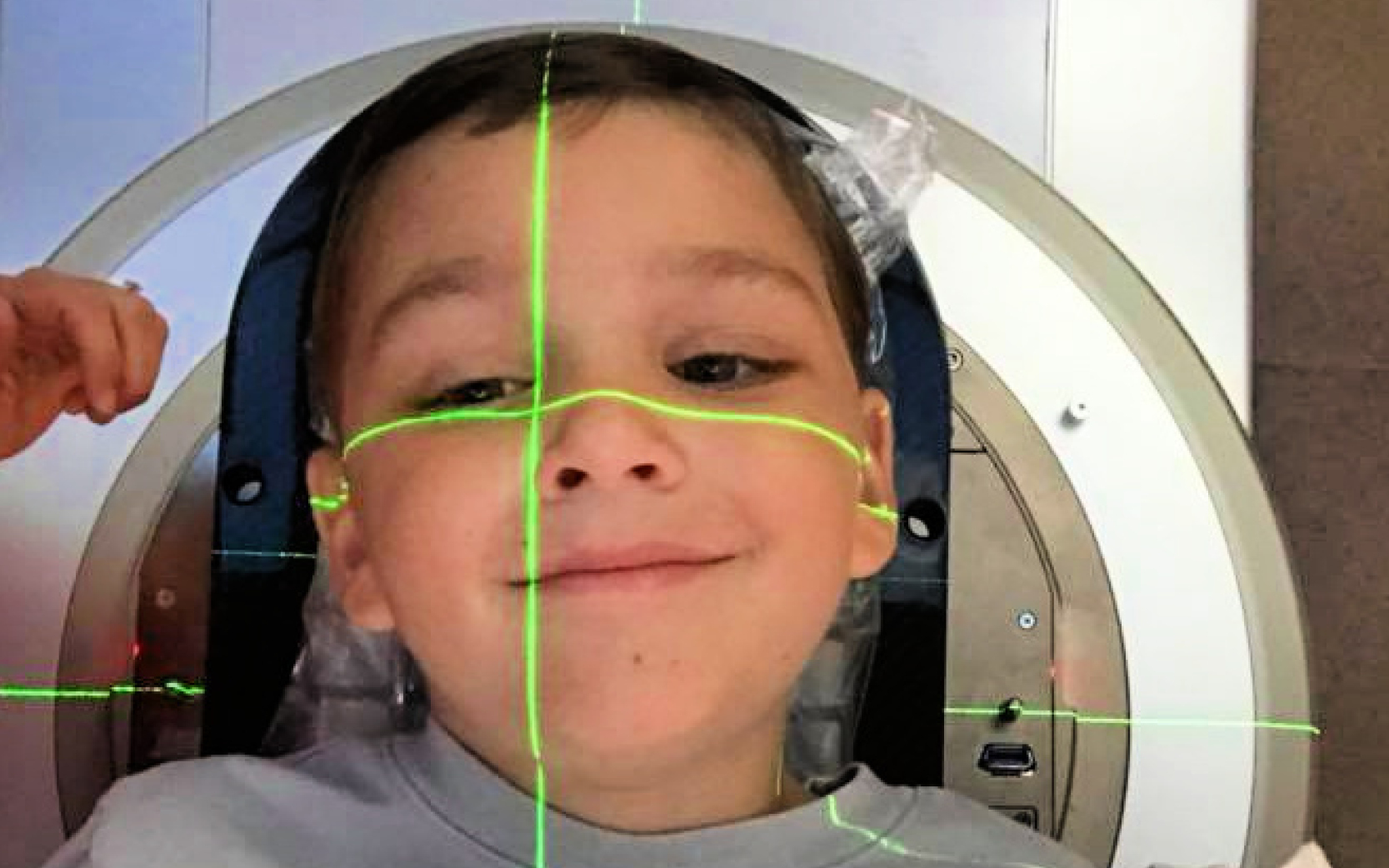
Kids Get Different Cancers Than Adults
Adults tend to get lung, breast, prostate and colon cancers, while kids are diagnosed with different cancers such as brain tumors, solid tumors and leukemia. Different cancers mean kids need different research and treatments.
Types of Childhood Cancer

Brain tumors are the most prevalent form of pediatric cancer in kids under the age of 19. Brain cancer can form in any area of the central nervous system, which is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Certain types are more likely to occur in certain parts of the brain. Medulloblastoma is the most common malignant brain tumor, accounting for about 20 percent of all pediatric brain tumors. Other common childhood brain tumors include atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors (ATRT), primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNET) and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG).




While rare pediatric cancers are difficult to research, we are committed to finding better treatments for all types of childhood cancers. Some uncommon cancers include: adrenocortical carcinoma, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML), colon cancer, esthesioneuroblastoma, liver tumors (hepatoblastoma and hepatocellular carcinoma), malignant rhabdoid tumors, melanoma, nasopharyngeal cancer, pleuropulmonary blastoma (PPB) and thyroid tumors, just to name a few.
Ways Childhood Cancer is Treated
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy consists of anti-cancer drugs as part of an ongoing regimen designed to cure, control and/or alleviate the symptoms of cancer.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy utilizes a child’s own immune system to target and treat cancer.
One example of immunotherapy treatment is CAR-T cell therapy, which takes a patient’s T cells, or cells found in the immune system, and genetically modifies them in the laboratory to attack the cancer cells
Molecularly Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy drugs work by blocking the growth and spread of cancer
by interfering with specific molecules that are involved in the progression of
cancer. Blocking these molecules can kill cancer cells or can keep cancer cells
from growing or spreading.

Proton Radiation
Proton therapy, also called proton beam therapy, is a type of radiation therapy
that uses protons, rather than x-rays, to treat cancer. Compared with x-ray
radiation therapy, proton therapy delivers up to 60% less radiation to healthy
tissues around the tumor.
Radiation
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high doses of radiation to kill
cancer cells and shrink tumors.

What is ALL?

What is DIPG?